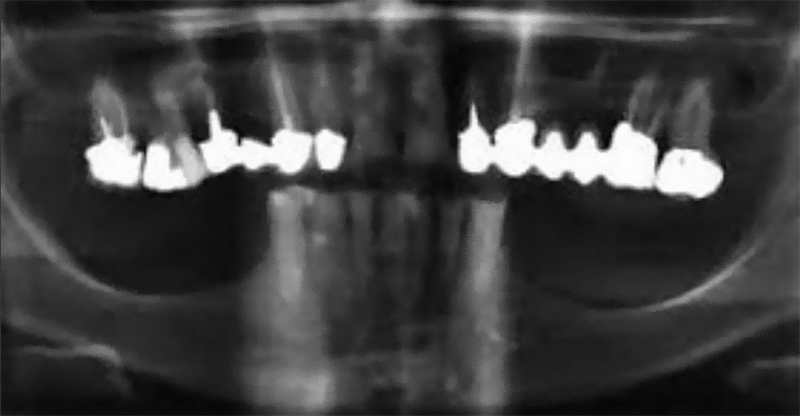
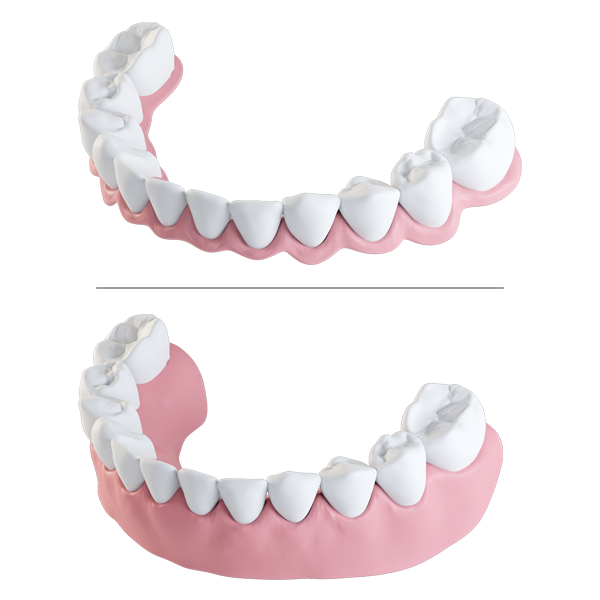
Rehabilitation of mandibular atrophy is a major challenge in oral implantology. Techniques such as vertical bone augmentation grafts or transposition of the dental nerve have been reported but with significant postoperative risks: bone resorption, severe pain or loss of sensitivity(1).
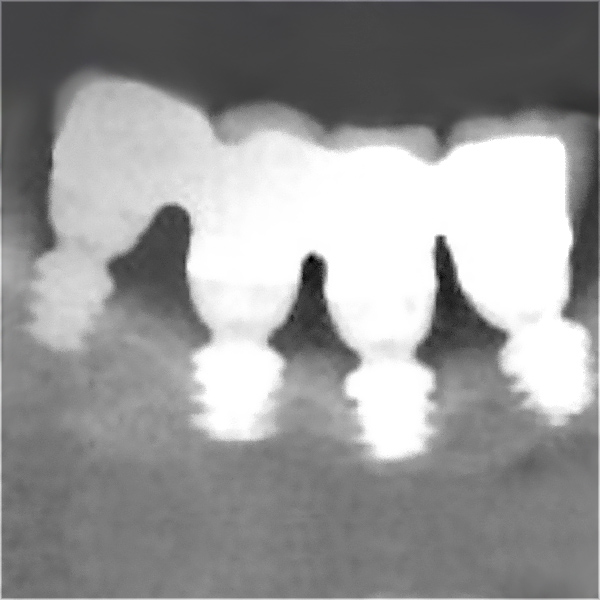
Alternatively, many 8-year studies show that it is possible to obtain satisfactory or better clinical results with comparatively short implants rather than longer implants placed in the augmented bone(2).
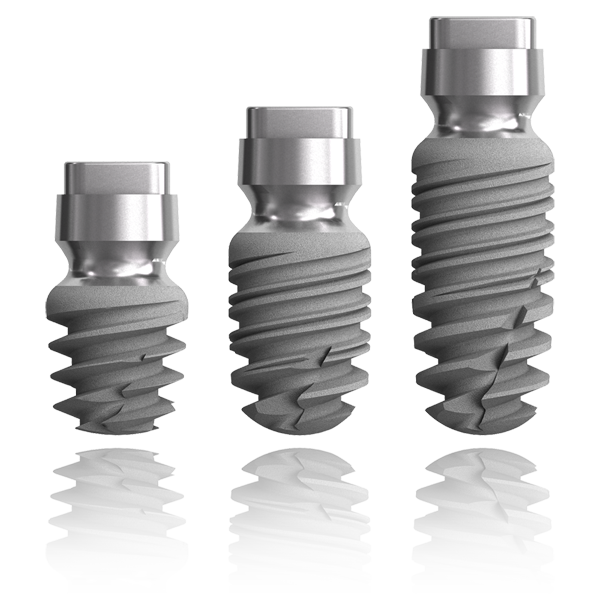
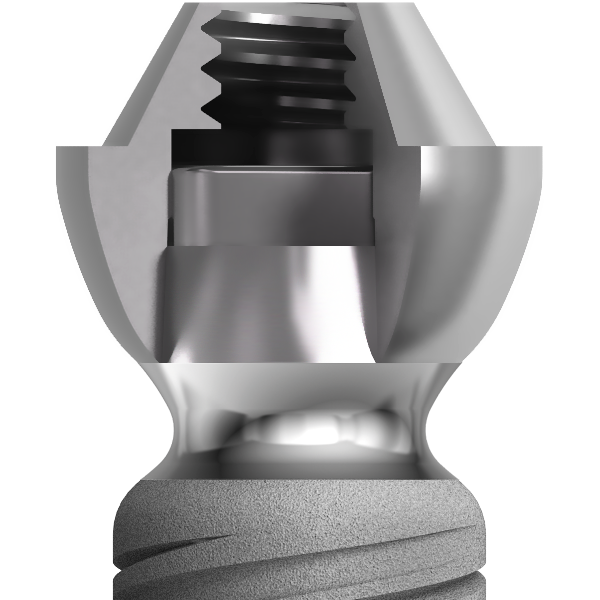
Revised Tissue Level
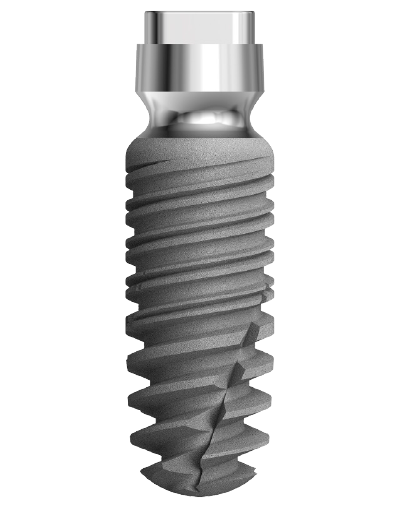
The twinKon® has a rounded shoulder at the limit of the roughened area of the implant. This shoulder is surmounted by a smooth concave collar in contact with the junctional tissue. The aim of the concave collar is first to recreate a mucosal seal which will act as a natural barrier. All subsequent prosthetic manipulation will take place above this limit, therefore reducing the risk of iatrogenic contamination with the benefit of preservation of the residual bone.
Concave collar and tissue reorganisation
In a study on dogs, Doctor Caroline Bolle demonstrated that after 12 weeks, there was reorganisation of the connective tissue which was rich in fibroblasts and collagen fibres anchored in the bone and converging horizontally on the implant. In the healing space defined by the concavity of the transmucosal collar, circular horizontal organisation of the collagen fibres was observed with a thickness of 500 mm (from the collar to the edge). On a small scale, vertical slices revealed dense circumferential formation of the collagen fibres.
C. Bolle– Early Periimplant Tissue Healing on 1-Piece Implants with a Concave Transmucosal Design: A Histomorphometric Study in dogs (2015)