Orthodontic treatments in children
The age of children or adolescents partially determines the type of orthodontic or orthopaedic dentofacial treatment required to resolve poor tooth positioning, malocclusions, problems with size and position of jaws, etc.
From the age of four, children can have orthopaedic treatment to resolve problems with poor tooth positioning via complete repositioning (crown and dental root) of poorly positioned teeth.
Treatments can mainly be carried out in children from the age of 7 to correct problems with abnormal jaw development (excessive growth or poor growth), lack of balance between the maxilla and mandible, palate deformation and misalignment of upper and lower teeth.
From the age of 11, with implantation of adult teeth on the dental arch, orthodontic treatments can enable final alignment of teeth with dedicated devices, repositioning of teeth by rotation or correction of misalignment of jaws during growth.
Orthodontic treatments in adults
After adolescence, orthodontic treatments can be performed for aesthetic reasons (alignment of poorly positioned teeth), but most frequently for correcting problems with occlusion (overbite/underbite, supraocclusion, subocclusion, etc.).
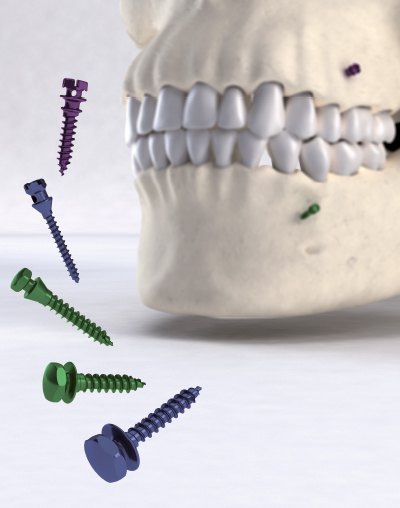
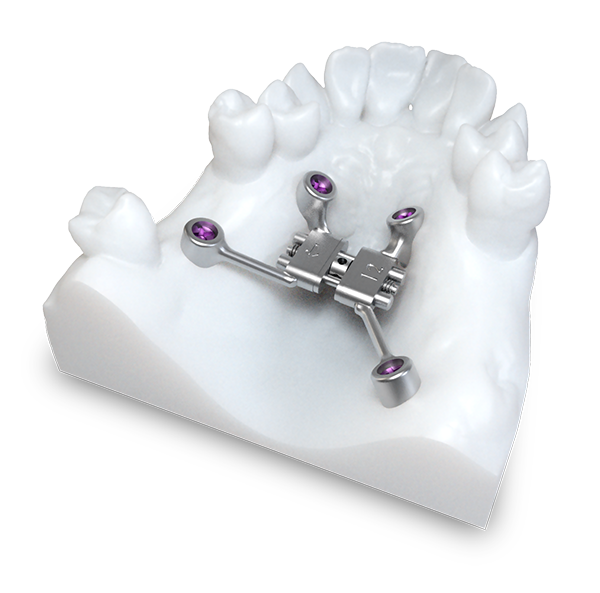
Although in children orthodontic treatments are usually performed using fixed, removable or partially removable orthodontic devices, in adults and for treatments requiring significant dentofacial orthopaedic work, bone anchorages with base mini-screws and anchorage plates are used.
Finally, in adults, as growth is complete, it is no longer possible to change jaw position or size by dentofacial orthopaedic treatment, and maxillofacial surgery is required.